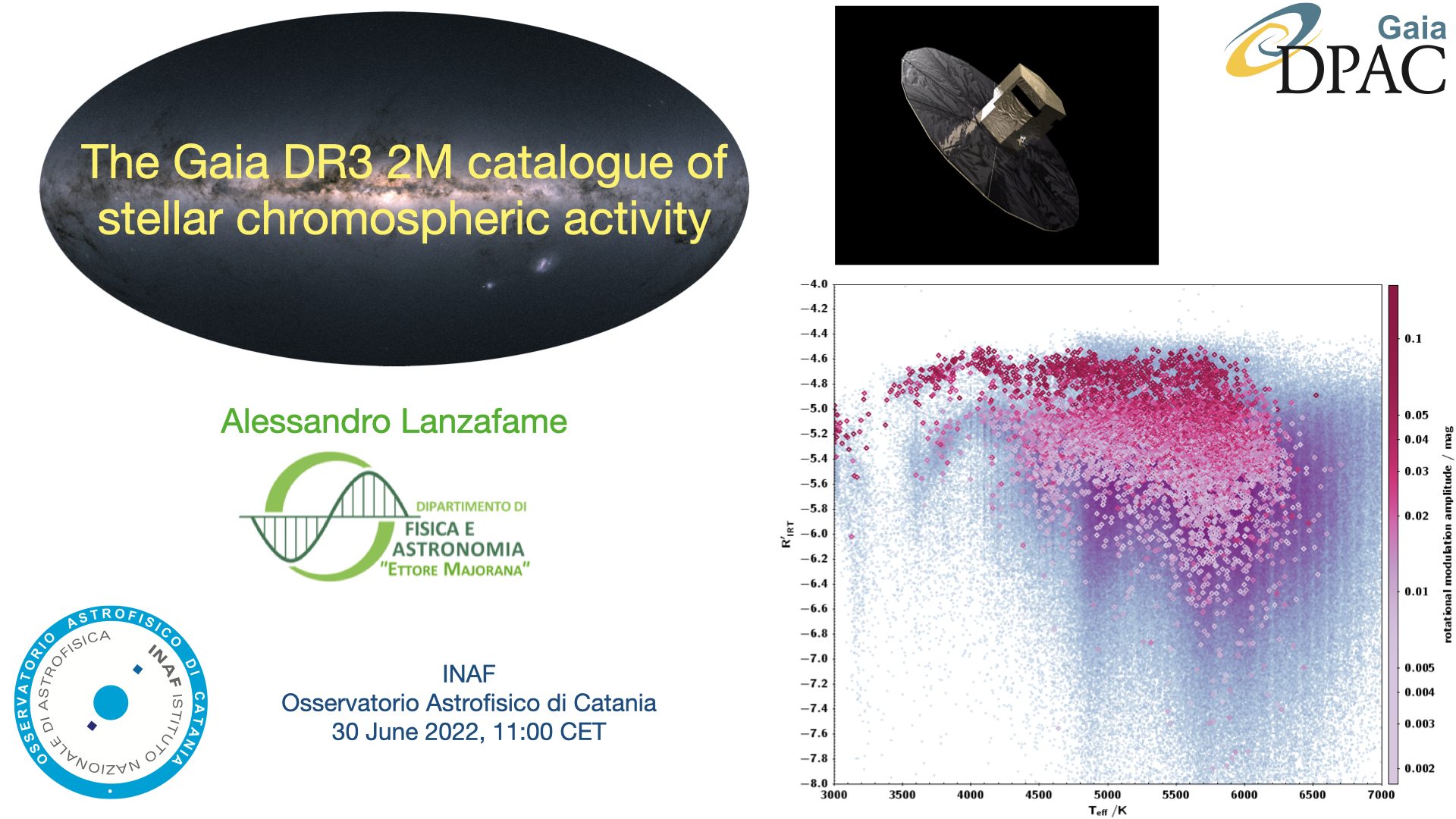
We present the method devised for inferring the Gaia stellar activity index from the analysis of the Ca II infrared triplet (IRT) at 850.03, 854.44, and 866.45 nm in the Gaia Radial Velocity Spectrometer (RVS) spectrum, an overview of the content of the chromospheric activity catalogue published in DR3, and its scientific validation. A sample of well studied PMS stars is considered to identify the regime in which the Gaia stellar activity index may be affected by mass accretion. The correlation with the amplitude of the photometric rotational modulation is also discussed. Three regimes of the chromospheric stellar activity are identified, confirming suggestions made by previous authors on much smaller chromospheric activity indices datasets. The highest stellar activity regime is associated with PMS stars and RS CVn systems, in which activity is enhanced by tidal interaction. Some evidence of a bimodal distribution in MS stars with Teff > 5000 K is also found, which defines the two other regimes, without a clear gap in between. Stars with 3500 K < Teff < 5000 K are found to be either very active PMS stars or active MS stars with a unimodal distribution in chromospheric activity. A dramatic change in the activity distribution is found for Teff < 3500 K, with a dominance of low activity stars close to the transition between partially- and fully-convective stars and a rise in activity down into the fully-convective regime. Overall, the 2M catalogue of chromospheric activity in Gaia DR3 represents a gold mine for studies related to stellar magnetic activity and mass accretion in the solar vicinity.