This month, NEANIAS has officially released its first version of space services. These services tackle some of the most important needs of the space research community, focusing on three main areas: data management and visualization (SPACE-VIS), map making and mosaicking (SPACE-MOS) and pattern and structure detection (SPACE-ML).

The SPACE-VIS service provides an integrated operational solution for astrophysics and planetary data management, aided by advanced visualization mechanisms, including visual analytics and virtual reality, and underpinned by FAIR principles. These are the basic pillars of NEANIAS and the whole EOSC, key for Open Science: Findability, Accessibility, Interoperability, and Reproducibility.
We exploit ViaLactea service to utilise astrophysical surveys to understand star formation processes into our galaxy, the Milky Way. ViaLactea Visual Analytics (VLVA) combines different types of visualization to explore and analyse data and discover correlations, taking advantage of the ViaLactea Knowledge Base (VLKB). VLKB includes 2D maps and 3D data cubes from a number of Galactic Plane surveys, as well as numerical model outputs, point-like, extended and diffuse object catalogues.
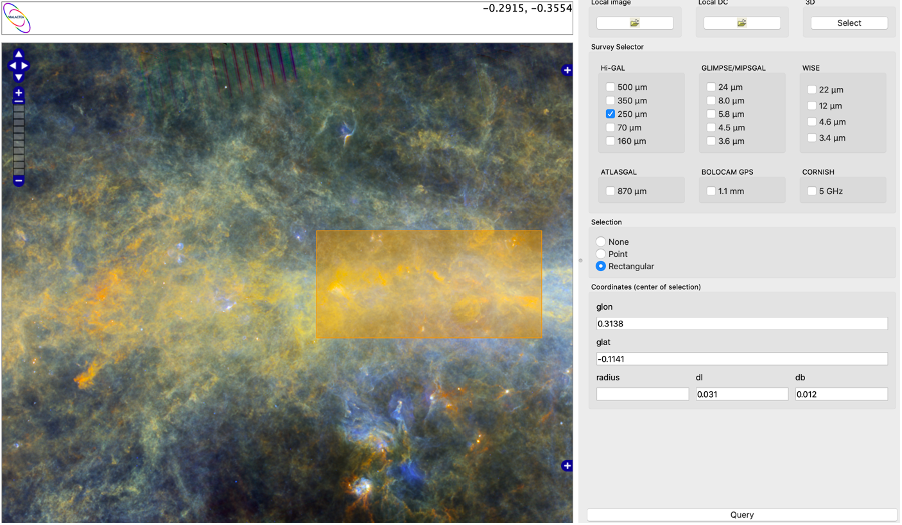
The ViaLactea service
The Astra Data Navigator (ADN) service is a virtual reality environment for visualizing large stellar catalogues, such as those produced by the Gaia mission. The released first version has been customised to access cloud services for interactive data exploration and navigation.

The Astra Data Navigator service
Finally, when it comes to studying planets, the Advanced Geospatial Data Management platform (ADAM) provides access to a large variety of environmental data from Earth. It has been customised in NEANIAS to also deliver planetary data provided by PlanetServer.
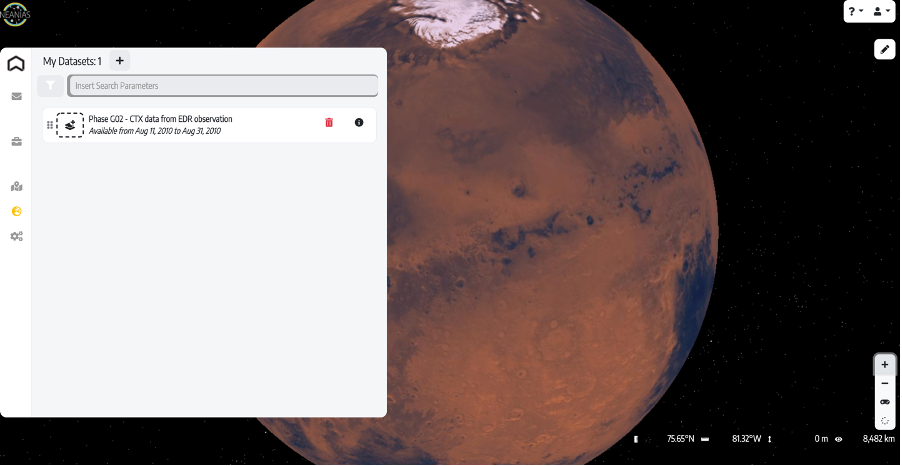
The ADAM-Space service

The service is based on the commonly used library Montage, and is integrated with VLKB for merging adjacent datasets. SPACE-MOS also allows for integration with data processing pipelines in ADAM, offering tools for planetary data analysis and for producing cartographic products, such as Digital Elevation Models (DEMs) and 3D models from stereo imagery.

The spearhead of SPACE-ML, the CAESAR service, is able to extract and parameterise compact and extended sources from astronomical radio interferometric maps, such as those produced by SKA precursors. The CAESAR pipeline consists of a series of independent processing stages (e.g. image denoising, background estimation, compact source removal…) that can run in parallel in multiple cores and processors, greatly enhancing the overall performance. As a final stage, NEANIAS has integrated a deep learning algorithm that significantly improves source identification, classification and characterisation. CAESAR functionalities can be accessed using a user-friendly web interface.
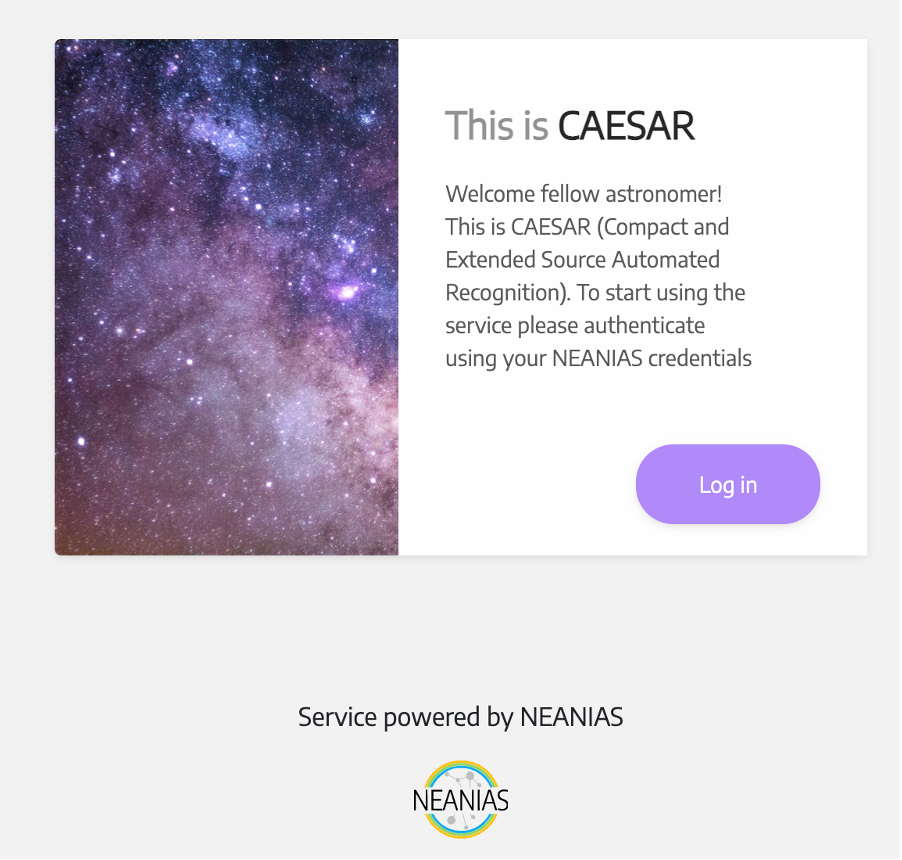
The CAESAR service
The NEANIAS space thematic services are reachable through the NEANIAS space portal: https://thematic.dev.neanias.eu/SPACE/.
All related documentation has been delivered on the NEANIAS documentation repository: https://docs.neanias.eu/en/latest/\#space-services and the relevant source code is handled by the NEANIAS GitLab repository: https://gitlab.neanias.eu/ .
Eva Sciacca & Cristobal Bordiu
Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica (INAF)
for the NEANIAS Space Team
